(1) ion implant 공정이란?
<WHAT>
: 반도체가 전기적 성질을 가질 수 있도록 carrier를 지닌 원자나 분자를 원하는 부위에 주입(doping)하는 공정.
<WHY>
: 트랜지스터 트렌드 변화 → ion implant 공정 적용이 필수가 됨.
① BJT → MOSFET.
| MOSFET | BJT |
| junction 깊이 얕음. | junction 깊이 깊음. |
| 소자 size 측면 anisotropic doping 반드시 필요. | - |
| doping이 필요한 layer 수가 점점 증가. | doping layer 수가 적음. |
② scaling down.
- 소자 크기와 동작 전압이 갈수록 scale down → junction depth도 함께 scale down해야 함.
→ shallow junction 필요. - total parasitic resistance는 active area channel resistance(=Rcontact+Rsource+Rext) 보다 훨씬 낮아야 함.
→ heavy doping 필요. - diffusion공정으로는 shallow junction과 heavy doping을 동시에 얻을 수 없음.
→ ion implant 공정 사용.
* diffusion 공정
: 확산에 의한 방법
- doping 필요한 영역을 photo 공정으로 open시킨 wafer를 chamber내에서 세워 넣음.
- 고온에서 오랜 시간 가열.
- 불순물이 Si 격자 사이사이로 확산, 침투.
| ion implant | diffusion | |
| advantage | ▶low temp process (PR mask). ▶precise dose control (1011~1016 /cm2). ▶accurate depth control and modeling. ▶independent control of dopant concentration and junction depth. ▶less lateral distribution → good for smaller feature size. |
▶no damage created by doping. ▶batch fabrication. ▶possible deep junction formation. |
| disadvantage | ▶implant damage enhances diffusion (TED). ▶dislocations caused by damage may cause junction leakage. ▶implant channeling may affect profile. ▶relative shallow max junction depth (~1μm) ▶low throughput |
▶high temp process (hard mask). ▶usually limited to solid solubility. ▶low surface concentration hard to achieve without a long drive-in. ▶low dose predeps very difficult. ▶no independent control of dopant concentration and junction depth. |

(2) ion implant parameter
1) dopant
- N형/P형 → 5족/3족 불순물.
- doping 깊이 → dopant의 질량에 따라 결정.
(깊으면 질량이 작은 dopant. 얕으면 질량이 큰 dopant.)
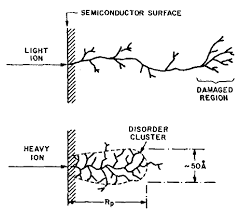
2) dose (주입량)
- doping 농도 결정.
- source/drain → 고농도.
- LDD, 채널 → 저농도.
3) energy (dopant를 가속하는 힘)
- doping 깊이와 내부 농도 profile 결정.
- energy↑ → 더 깊은 doping.
4) tilt (implant 하는 각도와 연관)
- doping 깊이와 위치 결정.
- 특정 위치 하부에 implant하는 경우 사용 (ex. HALO 공정)
→ 각도 매우 크게 틀어서 implant.
(3) implant후 anneal 공정
<WHAT>
: damage를 받은 Si 격자 구조를 정상 위치로 돌려놓기 위해 열처리 하는 것.
<WHY>
① damage를 치료.
: ion implant 공정 = ion을 가속하여 높은 운동에너지로 Si에 주입.
→ Si 결정 격자에 damage.
→ damage를 받은 원자들은 전기적으로 불활성 상태가 됨.
→ Si의 전기적 특성 나빠짐.
∴ 열처리를 통해 Si 격자 구조를 정상 위치로 돌려 놓는다.
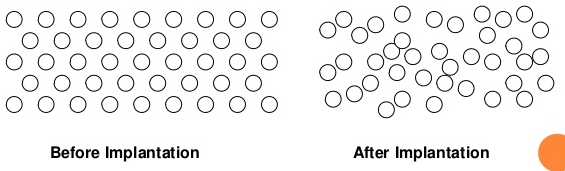
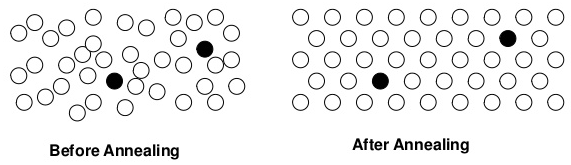
② 이온을 활성화.
→ doping된 불순물이 캐리어를 생성하는 역할을 하게 해준다.
③ doping 산포를 고르게 해줌.
∵ 열처리 과정에서 doping된 불순물이 Si 격자에 자리를 잡게 됨.
<HOW>
1) furnace anneal
2) RTP (rapid thermal process)
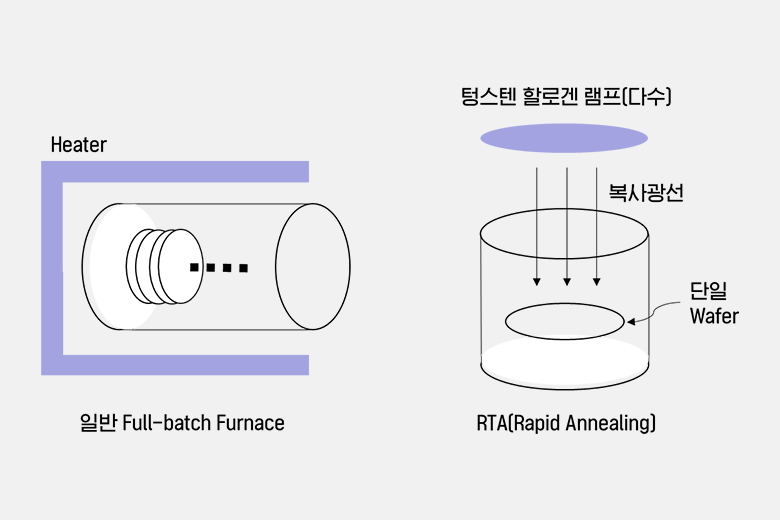
| furnace | RTP | |
| wafer 수 | 200~300매 (batch type) | 1매 (single-wafer type) |
| wall type | hot wall | cold wall |
| 공정 시간 | long time (30min at 850~1000℃) | short time (30sec at 1100~1150℃) |
| cycle time | long (4~5시간) | short (1분 이내) |
| 온도변화율 (dT/dt) | small (10℃/min) | large (100~300℃/sec) |
| issues | thermal budget particle atmosphere |
uniformity repeatability throughput wafer stress absolute temp |
*TED (transient enhanced diffusion)
- implant 공정에서 발생한 intersititial damage로 인해 dopant diffusion을 의도한 것보다 더 확산되는 현상.
- TED으로 인해 annealing 과정에서 원치 않는 dopant diffusion이나 cluster formation 발생.
- 최근에는 shallow profile을 갖기 때문에 junction depth를 결정하는 데에 큰 영향을 미친다.
- 낮은 온도에서 더 많이 확산되는 이례적인 diffusion 현상이다.
∵ 저온에서 TED 현상이 더 오래 지속됨.
→ TED를 억제하기 위해 고온에서 빠르게 끝나는 RTP 적용.
<참고문헌>
이창훈, 반도체 소소제공, 더인 출판사, 2019, pp.178-186.
최리노 교수, '반도체공정 ion implantation' 강의 ppt, 인하대학교.
진종문, [반도체특강]웨이퍼를 담금질하다: 파괴를 복원하는 어닐링, SK하이닉스 뉴스룸, 2018.
'반도체 > 반도체 공정' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 16. diffusion 공정 & oxidation 공정 (0) | 2020.06.29 |
|---|---|
| 15. ion implant 공정(2) (문제점, 검사법, 장비) (4) | 2020.06.17 |
| 13. cleaning 공정(2) (오염물질의 종류) (1) | 2020.06.09 |
| 12. cleaning 공정(1) (목적, 방식) (0) | 2020.06.05 |
| 11. Plasma (정의, 생성원리, 활용원리) (0) | 2020.06.02 |


